Analyzing a sentence grammatically means breaking it into clear parts so you can understand how each word works. When you analyze a sentence the right way, you understand its structure, meaning, and correctness. This skill improves writing, reading, and communication. It is used by teachers, students, editors, language experts, and anyone who wants clean, correct English. This guide explains how to analyze grammatically as a sentence in the simplest possible way, step by step.
What Does It Mean to Analyze Grammatically as a Sentence?
To analyze grammatically as a sentence means to study every part of a sentence and identify:
-
Who or what is doing the action
-
What action is happening
-
How the other words support the meaning
-
How phrases and clauses connect
-
What rules of grammar the sentence follows
This process is also called parsing. Parsing helps you see:
-
Sentence patterns
-
Word functions
-
Sentence errors
-
Meaning relationships
When you finish analyzing a sentence, you should know exactly how the sentence works from start to end.
Why Grammar Analysis Is Important
Grammar analysis helps you:
-
Write clearly and professionally
-
Avoid grammar mistakes
-
Understand complex sentences
-
Improve speaking and writing skills
-
Score higher in school or exams
Even powerful language tools use grammar analysis. Human readers and digital systems understand sentences faster when grammar is clear.
Steps to Analyze Grammatically as a Sentence
Below is a complete method anyone can follow.
Step 1: Find the Subject and Predicate
Every sentence has two main parts:
-
Subject – who or what the sentence is about
-
Predicate – what the subject does or what happens
Example:
The dog barked loudly.
-
Subject: The dog
-
Predicate: barked loudly
Once you find these two parts, the sentence becomes easier to understand.
Step 2: Identify the Main Verb
The main verb shows the action or state.
Examples:
-
runs
-
is singing
-
had gone
-
will arrive
The verb controls the meaning. Without it, you cannot have a complete sentence.
Step 3: Look at Objects and Complements
Objects receive the action. Complements add extra meaning.
Types of objects:
-
Direct object → receives action (He reads books.)
-
Indirect object → benefits from action (He gave her a gift.)
Types of complements:
-
Subject complement → renames or describes subject
-
Object complement → modifies the object
Complements help complete the meaning.
Step 4: Break the Sentence into Phrases
A phrase is a group of words without a subject-verb pair.
Common phrase types:
-
Noun phrase: the tall man
-
Verb phrase: has been running
-
Prepositional phrase: in the room
-
Gerund phrase: swimming in the lake
-
Infinitive phrase: to learn quickly
Phrases add detail and improve clarity.
Step 5: Identify Clauses
A clause contains a subject and a verb.
Clause types:
-
Independent clause → can stand alone
-
Dependent clause → cannot stand alone
Example:
Because he was tired, he went home.
-
Dependent clause: Because he was tired
-
Independent clause: he went home
Understanding clauses helps you analyze sentence structure.
Step 6: Determine the Sentence Structure
English has four main structure types.
| Structure Type | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Simple | 1 independent clause | She reads. |
| Compound | 2+ independent clauses | She reads, and he writes. |
| Complex | 1 independent + 1 dependent clause | She reads because she loves stories. |
| Compound-Complex | 2 independent + 1 dependent clause | She reads, he writes, and they learn because they practice. |
Knowing the structure helps you understand the flow of ideas.
Step 7: Check for Grammar Accuracy
Look for:
-
Subject-verb agreement
-
Correct verb tense
-
Proper word order
-
Clear modifiers
-
Correct punctuation
Sentence analysis also helps detect errors early.
See More: Sad Story 3 Words: Powerful Mini Stories That Carry Deep Emotions
Things to Always Check When Analyzing a Sentence
-
Subject
-
Verb
-
Object
-
Complement
-
Phrases
-
Clauses
-
Sentence type
-
Punctuation
-
Meaning clarity
Common Errors You Can Detect Through Grammar Analysis
-
Fragments
-
Run-on sentences
-
Comma splices
-
Misplaced modifiers
-
Wrong verb tense
-
Unclear pronoun reference
-
Incorrect prepositions
Practical Examples of Sentence Analysis
Below are simple examples that show how to analyze grammatically as a sentence.
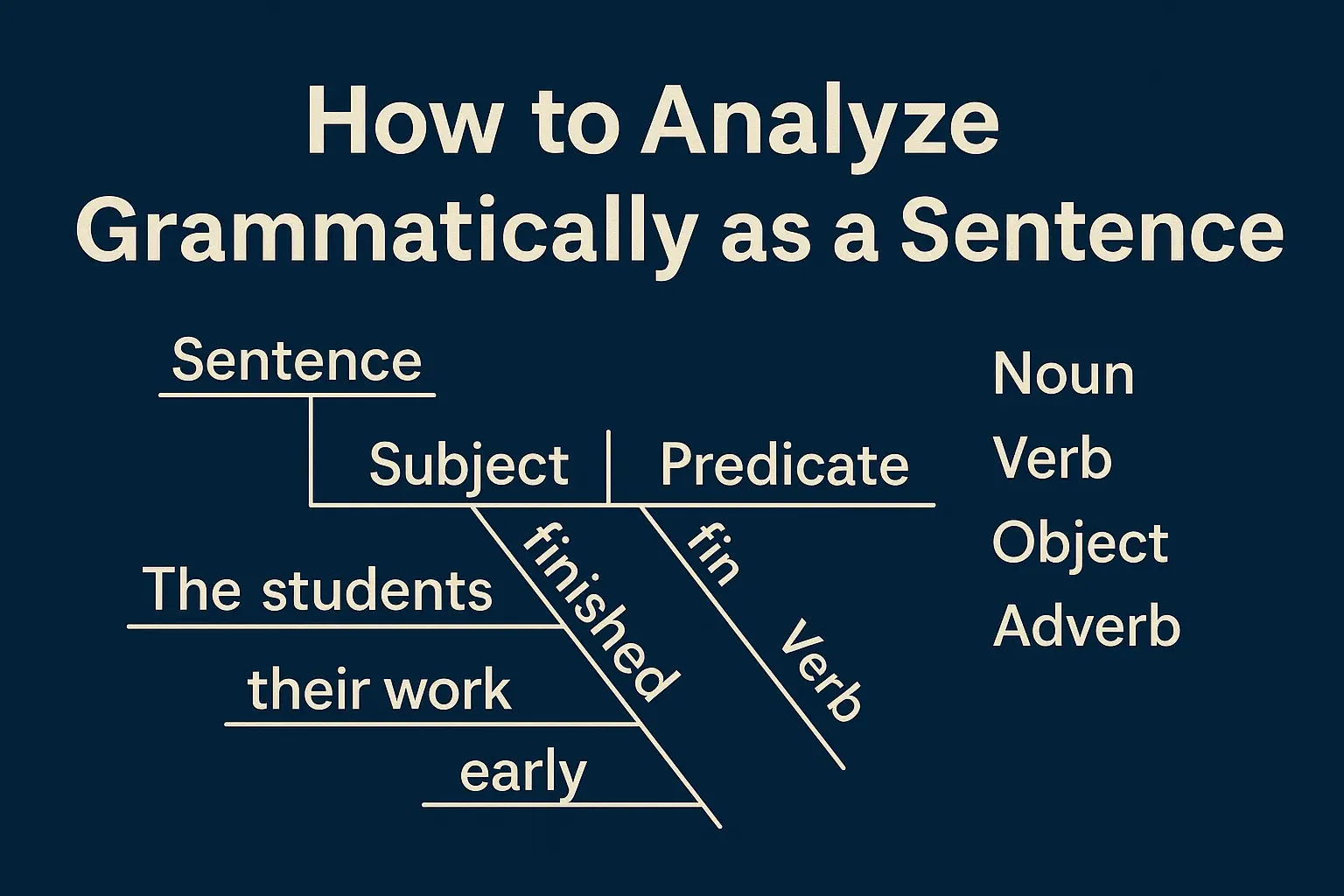
Example 1:
The students finished their work early.
-
Subject: The students
-
Verb: finished
-
Object: their work
-
Phrase: early (adverb)
-
Structure: Simple sentence
Example 2:
When the rain stopped, we continued the game.
-
Dependent clause: When the rain stopped
-
Independent clause: we continued the game
-
Structure: Complex sentence
Example 3:
The teacher explained the lesson, and the students asked questions.
-
Clause 1: The teacher explained the lesson
-
Clause 2: the students asked questions
-
Connector: and
-
Structure: Compound sentence
Advanced Tips to Analyze Grammatically as a Sentence
These tips help users achieve deeper accuracy.
1. Check the Function of Each Word
Words may look similar but work differently.
Example: fast can be an adjective or adverb.
2. Understand Logical Connections
Words like because, although, unless, and while show relationships.
3. Review Modifier Position
Misplaced modifiers create confusion.
Correct example: She nearly drove for ten hours.
Incorrect example: She drove for nearly ten hours. (meaning changes)
4. Use Grammar Tools Only as Support
Tools can help but cannot replace human understanding.
Quick Breakdown of Grammar Elements
| Grammar Element | Purpose | Key Questions |
|---|---|---|
| Subject | Names the topic | Who is acting? |
| Verb | Shows action/state | What is happening? |
| Object | Receives action | What is affected? |
| Complement | Adds meaning | What completes the idea? |
| Phrase | Adds detail | What group supports meaning? |
| Clause | Shows structure | Does it stand alone? |
| Modifier | Adds description | What word is clarified? |
See More: What Is an Occasional Teacher: Complete Definition, Duties, and Career Guide
FAQs About “Analyze Grammatically as a Sentence”
1. What does analyze grammatically as a sentence mean?
It means breaking down a sentence into parts such as subject, verb, objects, phrases, and clauses to understand how the sentence is formed.
2. Why is sentence analysis important?
It improves writing, grammar accuracy, reading skills, and clear communication.
3. Who uses grammar analysis?
Students, teachers, editors, proofreaders, content writers, IELTS candidates, and language learners.
4. Can simple sentences also be analyzed?
Yes. Even the shortest sentences contain important elements that can be examined.
5. What is parsing in grammar analysis?
Parsing is the process of identifying the function of each word and phrase within a sentence.
6. How can I improve my grammar analysis skills?
Practice daily, review sentence patterns, study clause types, and analyze sample sentences.
7. What tools support grammar analysis?
Grammar checkers, sentence diagram tools, linguistic software, and educational apps.
8. What is the most common mistake in sentences?
Subject-verb agreement errors are among the most common mistakes.
9. Can grammar analysis help in academic writing?
Yes. It ensures clarity, correctness, and strong sentence structure.
10. Is grammar analysis useful for non-native speakers?
Yes. It helps learners understand sentence rules and write clearly.
Conclusion
Analyzing grammatically as a sentence is a simple but powerful skill. It helps you understand exactly how English sentences work. By looking at the subject, verb, objects, phrases, and clauses, you gain complete control over grammar. This improves reading, writing, and communication. When you follow the steps in this guide, sentence analysis becomes easy, accurate, and effective.